As Machined
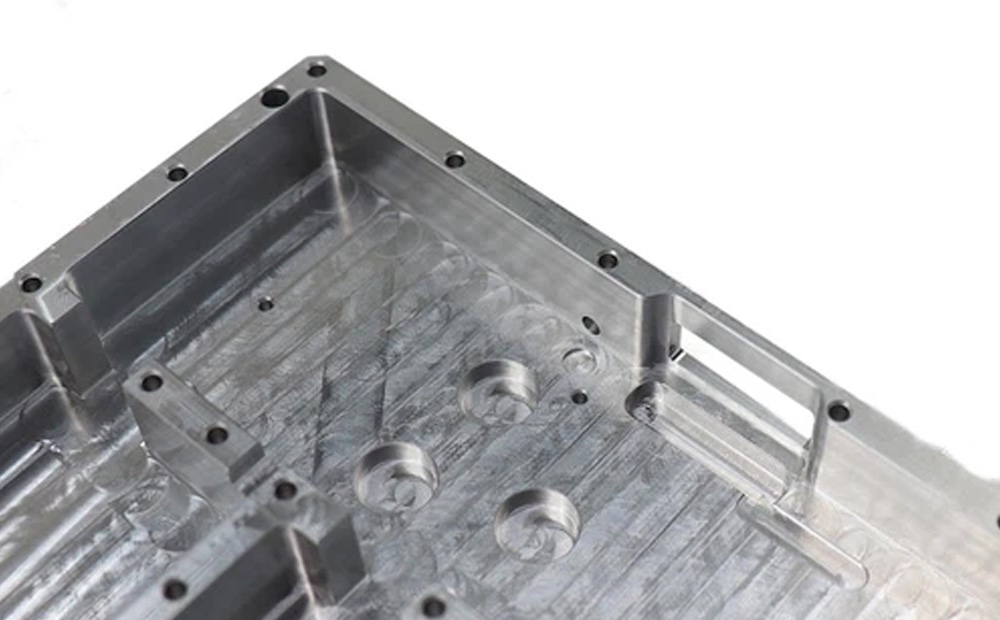

This machined finish is rough and shows tool marks. It is the simplest form of surface treatment. without additional finishing or polishing.
Anodizing

It creates a protective oxide coating on aluminum, enhancing corrosion resistance, hardness, and allowing for dyeing in various shades, thereby improving performance and appearance.
Polishing

It creates a smooth surface by removing flaws with abrasives, hence resulting in high gloss mirror finishes. Its major application is for aesthetic purposes while reducing friction.
Brushed Finish
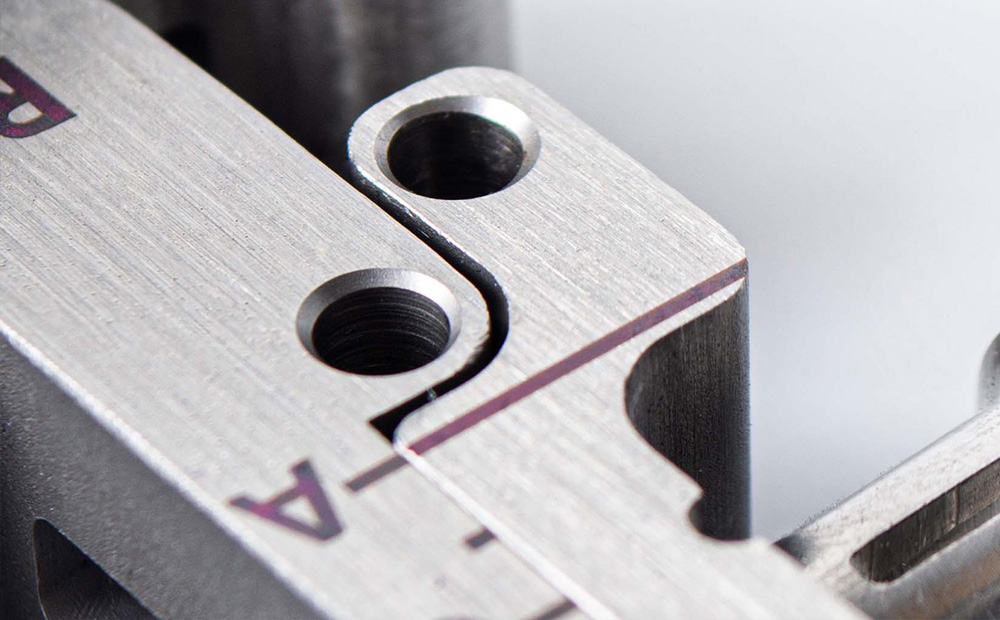

This texture can be achieved by rubbing abrasive pads on the surface. It gives it a matt appearance with grain directionality.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting cleans surfaces by propelling high-speed particles, resulting in a dull matte finish that enhances grip and prepares CNC parts for further finishing.
Electropolish
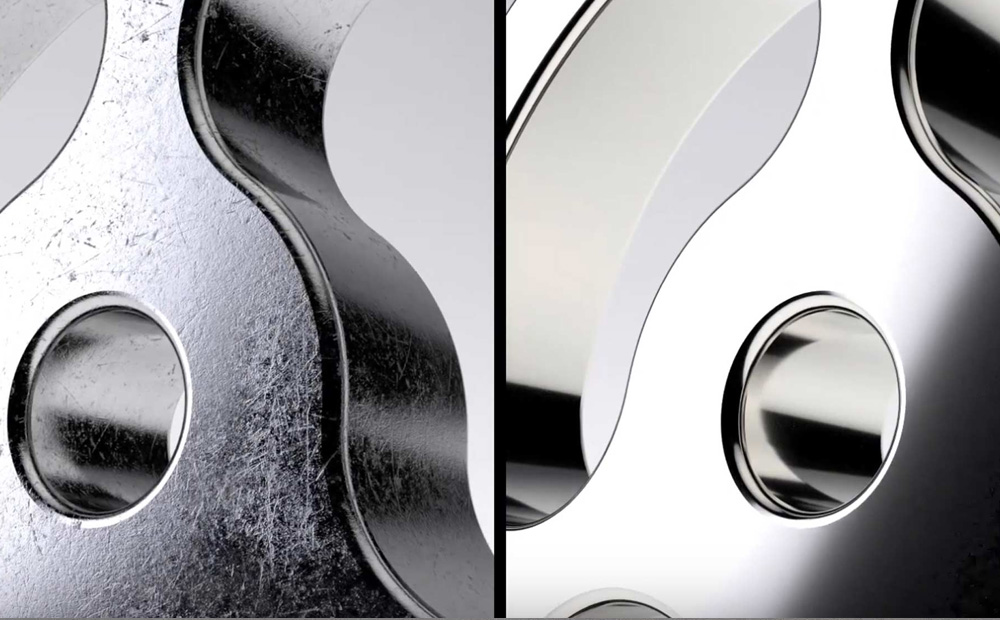

This process involves removing a material layer from a metal surface by electrochemical means. It improves smoothness and corrosion resistance. It’s mostly used on stainless steel.
Tumbling
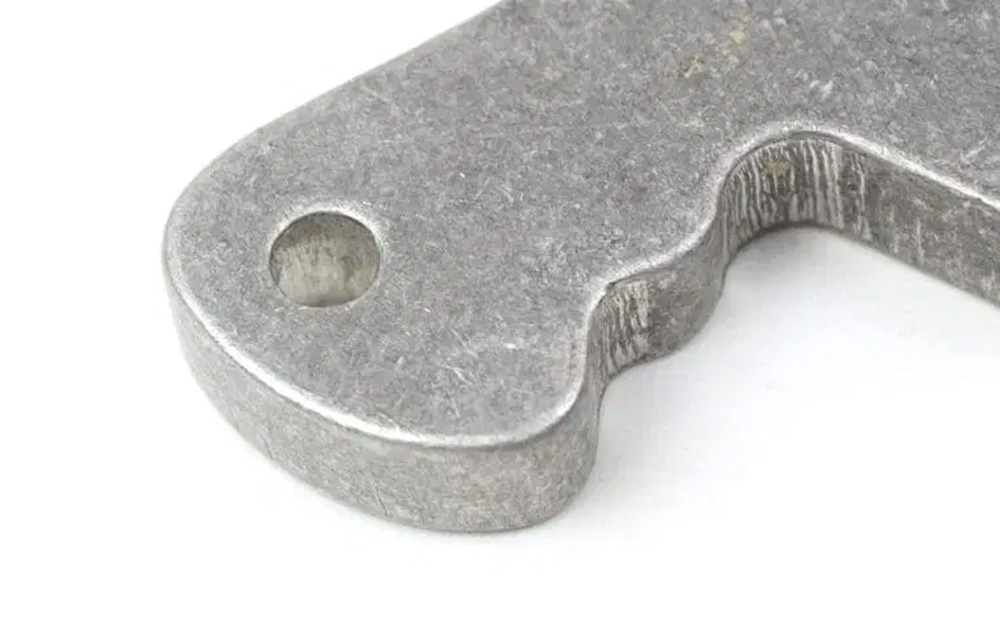

Tumbling involves putting components into a rotary barrel containing grit media to smoothen and polish them. This technique is efficient in cleaning and deburring ( removal of burrs) components.
Heat Treatment
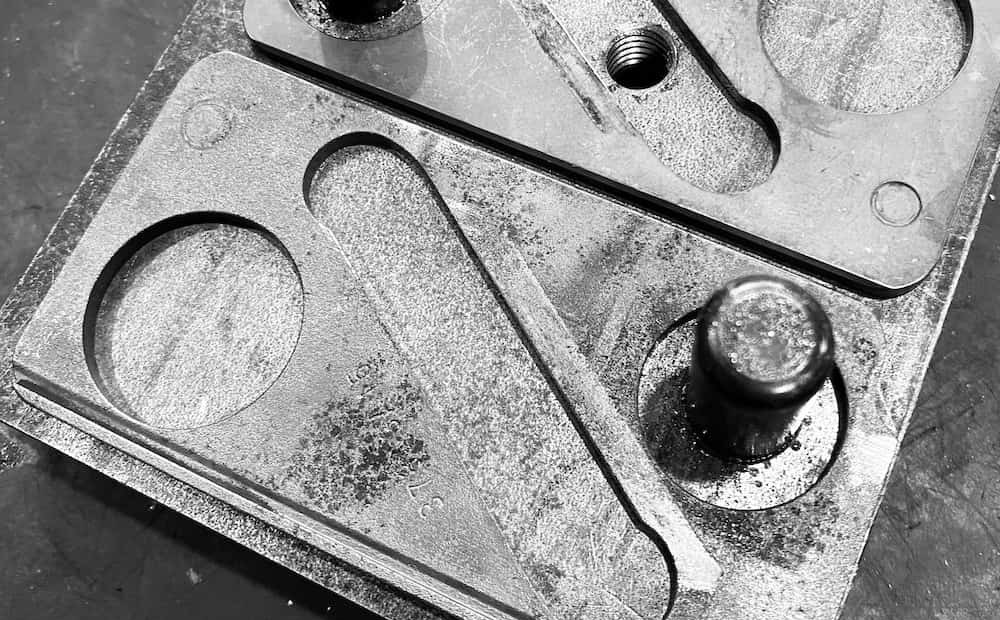

This is when you heat metals before cooling them to change their properties, such as strength, hardness, etc. Most of it deals with improving mechanical properties in metals.
Paint Coating
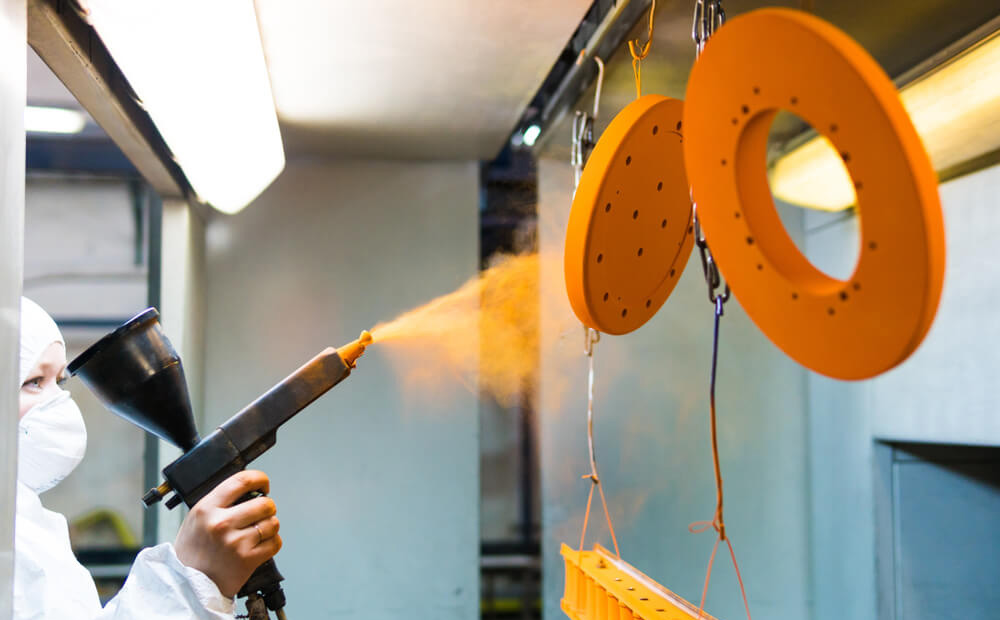

This process involves applying a protective or decorative layer of paint on a metal surface. It improves appearance, corrosion resistance, and weather protection. Commonly used on fabricated parts, machinery, and consumer goods.
Powder Coating
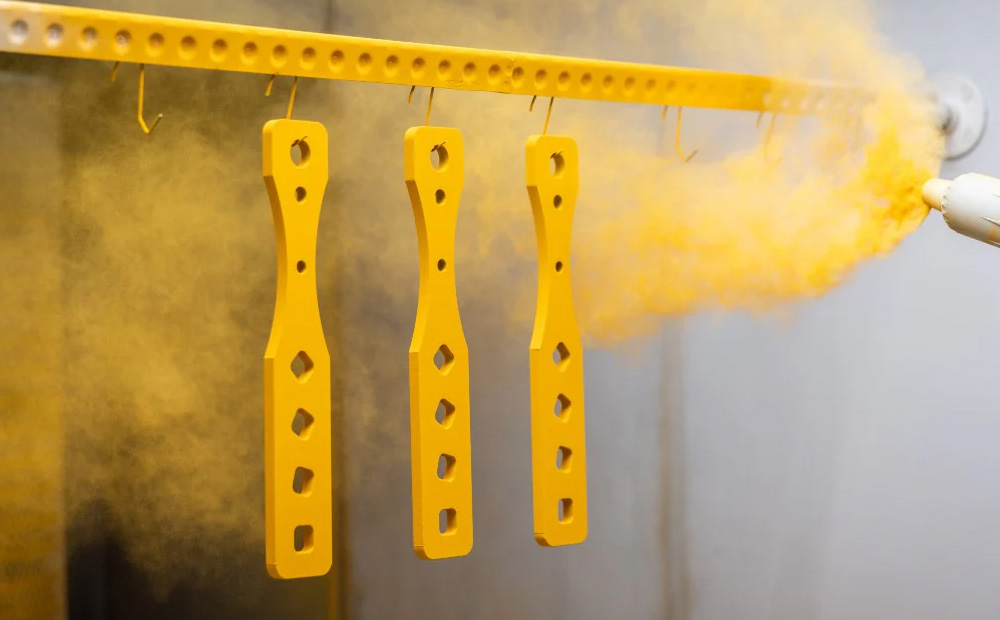

Powder coating involves spraying a dry powder onto surfaces and heating it to form a hard, durable, and evenly colored finish.
Electroplating
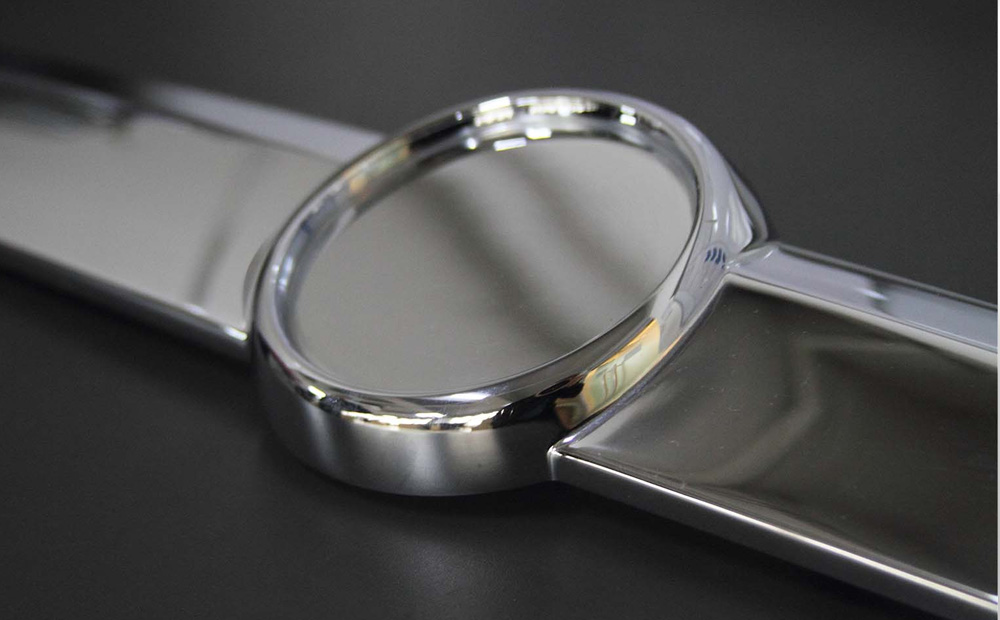

Electroplating is a process that uses electrical current to deposit a metal layer onto a surface, enhancing its appearance, corrosion resistance, and wear properties.
Black Oxidize
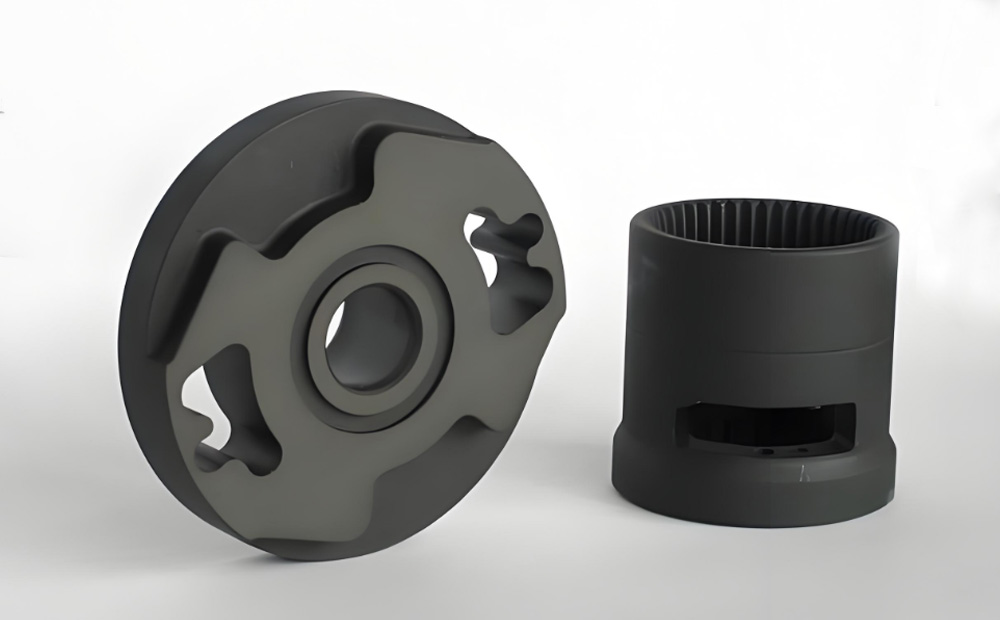

Black oxide coatings give certain metals dark finishes. They are more resistant to mild oxidation forms often sought for visual-only purposes.
Hot-dip Galvanizing
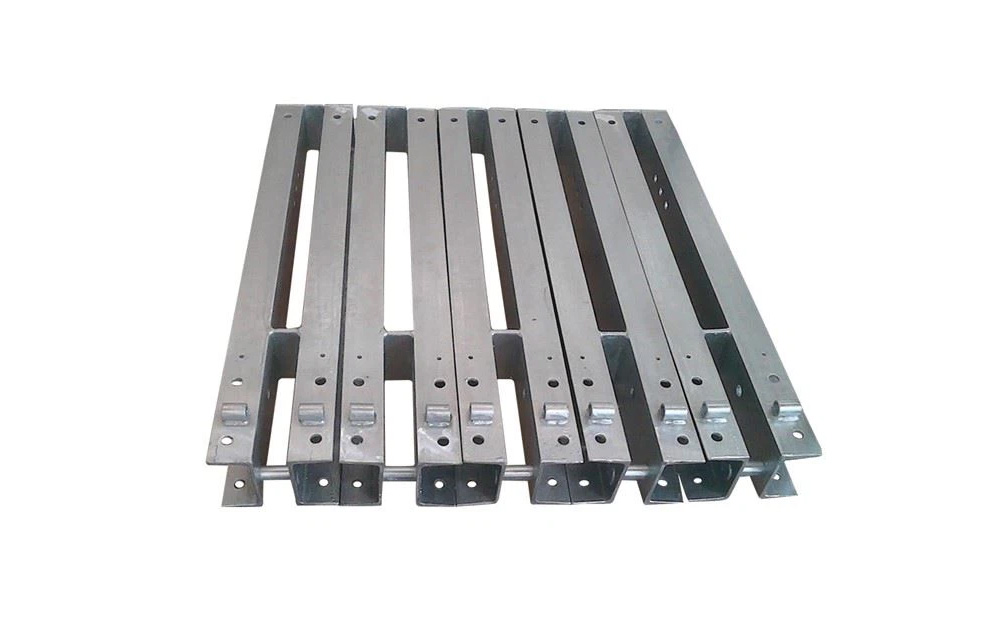

This process involves coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc by immersing it in molten zinc. It significantly enhances corrosion resistance and durability. It’s mostly used on structural steel, fasteners, and outdoor metal components.
Shot Blasting
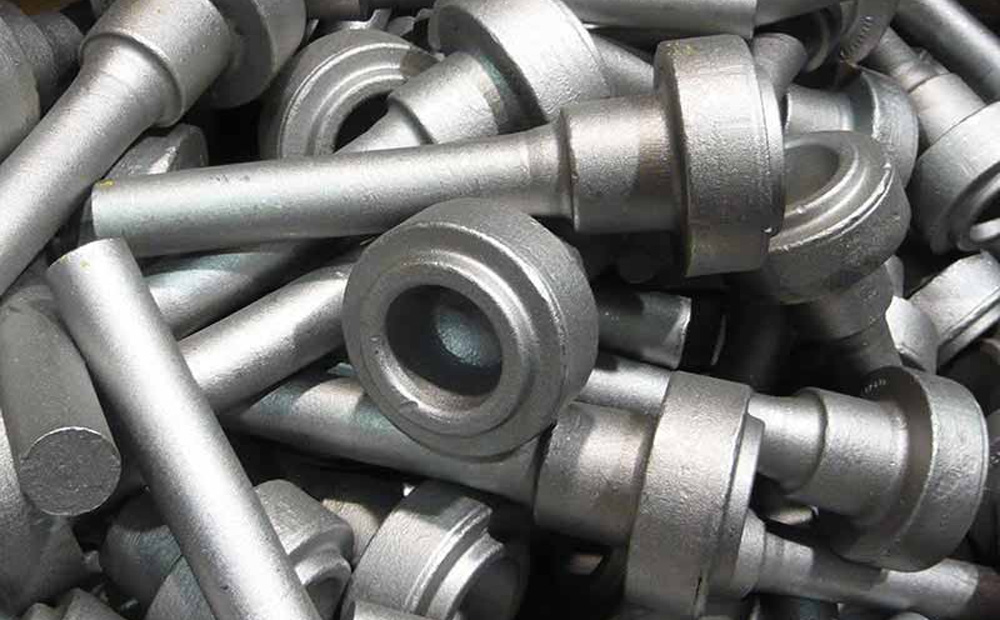

This process involves cleaning or preparing a metal surface by blasting it with high-speed abrasive particles. It removes rust, scale, and old coatings, creating a rough texture for better coating adhesion. Common for Forged parts.